Cord Blood vs. Cord Tissue vs. Cord Lining: What’s the Difference and Why Store Them All?
When parents think of stem cell banking, the first thing they often think about is cord blood banking. But there’s more to the umbilical cord than just blood. Inside the same cord lies cord tissue and cord lining, both rich in stem cells that hold incredible potential for future medical use.
If you’re an expecting parent preparing for your baby’s arrival, here’s a simple guide to help you understand the difference between cord blood, cord tissue, and cord lining, and why storing all of them with a trusted stem cell bank like Cordlife Philippines gives your family the most complete health protection.
What Is Cord Blood?
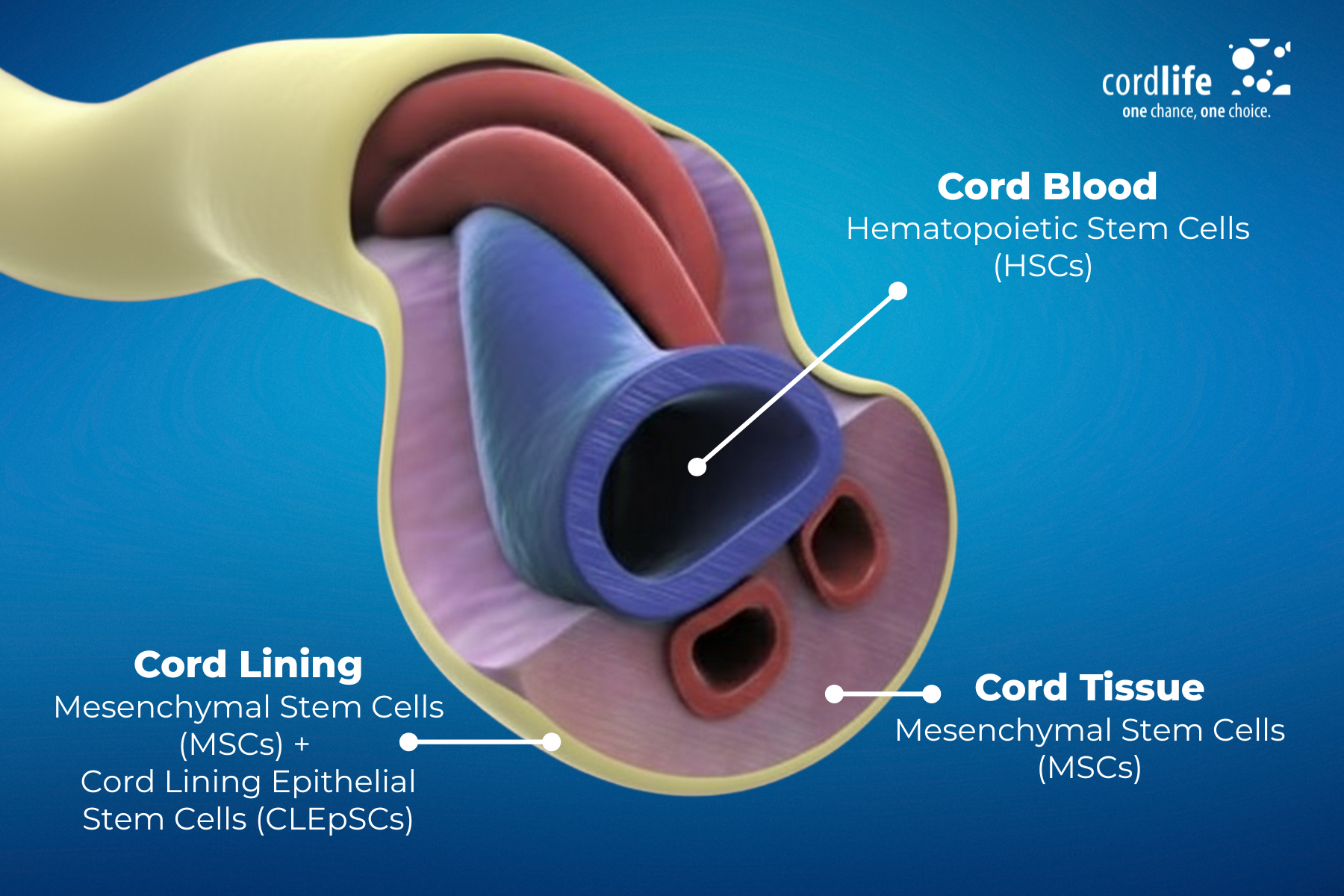
Cord blood is the blood left inside your baby’s umbilical cord and placenta after birth. It’s a rich source of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) - the building blocks of blood and the immune system.
These cells can be used to potentially treat over 80 diseases, including certain cancers like leukemia, blood disorders like anemia and thalassemia, and immune and metabolic disorders.
At Cordlife Philippines, your baby’s cord blood is processed and cryopreserved in the first and only ISO-certified and AABB-accredited laboratory in the Philippines, giving families peace of mind that samples are safely stored should your family ever need it for a transplant or treatment.
What Then Is Cord Tissue?
Cord tissue, on the other hand, refers to the gel-like material of the umbilical cord itself (also called Wharton’s Jelly). It contains a different type of stem cell, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which have the ability to develop into bone, cartilage, fat, and muscle cells.
MSCs are being studied for their potential in regenerative medicine, including therapies for heart disease, diabetes, stroke, spinal cord injury, and more.
Cordlife Philippines is one of the few stem cell banks in the Philippines that offers cord tissue banking, allowing families to benefit from the future potential of MSCs.
Okay, and Can You Tell Me About Cord Lining?
Cord lining, the outermost layer of the umbilical cord or what they refer as “the cord itself”, is another rich source of both cord lining epithelial cells (CLEpSCs) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), giving you a chance to store one more type of stem cells.
- Epithelial stem cells help with wound and soft tissue repair and eye conditions
- Mesenchymal stem cells support tissue repair, immune modulation or reconstruction
Cord lining stem cells are being explored for their potential in wound healing, skin regeneration, tissue repair, and immune-related conditions.
Why store all three?
Storing both cord blood and cord tissue gives your family a more comprehensive health protection:
- Cord blood (HSCs) treats blood and immune system and metabolic disorders
- Cord tissue (MSCs) offers regenerative potential to repair and regenerate tissues and organs.
- Cord lining (MSCs and CLEpSCs) gives you a chance to store another type of stem cells apart from MSCs which help with wound healing and eye disorders.
Together, they provide a powerful combination of healing and regeneration, addressing both current and emerging medical possibilities.
Future-Proofing Your Family’s Health
Medical research in stem cell therapy continues to evolve rapidly. By banking cord blood, cord tissue, and cord lining today, you’re not only safeguarding your child’s current health but also future-proofing your family’s access to life-changing medical innovations.
Cordlife Philippines’ advanced facilities, experienced biotechnologists, and medical experts ensure that your baby’s precious stem cells are in the best hands, starting from collection to storage.
Ready to Learn More?
Sit down with our Cordlife representatives to discover how you can secure cord blood, cord tissue, and cord lining banking for your family.
For a limited time this October, enjoy exclusive freebies and eGifts!
Recent Blog Posts
- 24 October 2025
- 24 October 2025
- 21 October 2025
- 09 September 2025
- 20 August 2025
